Why forex risk management is important for SME and Corporates today? The foreign exchange market is a global market for currencies that is estimated to be USD 5 Trillion per day as per Bank of International Settlements. For a business dealing and sourcing across the world, foreign exchanges bring their risks along with it.
What is Forex Risk? Why is forex risk management critical today?
Forex risk is the difference in the budgeted exchange rate and the actual exchange rate when a transaction is settled. For example, a chemical manufacturer imported certain Chemical worth USD 100,000 on Jan 15th and budgeted an exchange rate of 69 for USDINR. It takes about one month for him to receive goods and pay for them. By the time he pays, the exchange rate moves to 72, and he ends up paying Rs 72,00,000 as against the budgeted cost of Rs 69,00,000. Therefore because of movement in foreign exchange rates, he lost Rs 300,000. If the exchange rate had moved other way to 68, he would have gained Rs 100,000. So, because of movement in forex rate, the manufacturer carries a risk of increase or decrease in his product costing. So longer the time between a sale, shipping and payments, more likely that the manufacturer exporting goods to be hit by forex volatility.
To minimize the foreign exchange risk of loss, every business needs to have forex risk management practices in place. A lot of corporates are unable to put appropriate forex risk management policies, and they end up losing money and overshooting their budgeted costs.
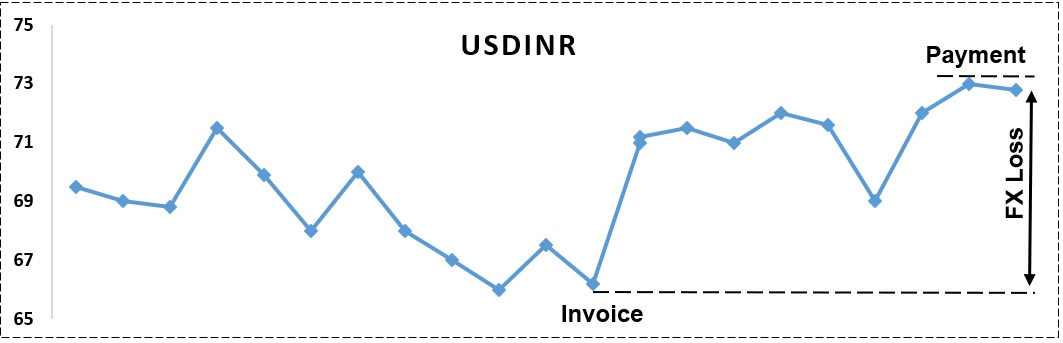
In the image shown above, an invoice was raised when Rupee was at 66, but when the payment was released, Rupee had depreciated to 73. The difference between two rates is Forex risk, and in this case, the risk results in a Loss.
One of the easier ways of eliminating forex risk is to receive payment only in your currency. But due to this, business cash flow risk may increase if your customer tries and time payments to get the advantage of exchange rate movements. Such a business may also lose customers to competitors who offer the flexibility of payments in foreign currency. Given the currency rates of each country are very closely interrelated to global developments, it may be worthwhile for a business to invest time and resources to create prudent risk management practices in place for their forex exposures.
Forex Risk Management Tips and Techniques:
Determine currency risk appetite in your business –
Each business has a different risk appetite for forex risk. Generally, business with low profitability finds it very difficult to withstand the adverse impact of currency fluctuations. Therefore one needs to decide how much fluctuation can one handle and accordingly decide forex hedging strategies. This can also help understand whether to put any risk management plan in place, if at all required. Eg. If you take a daily position equivalent to 20% of your investible surplus, how many times you need to lose the entire 20% to be bankrupt? Five times. So if you place 20% of your investible money in the market and lose all money(which is unlikely but not impossible) you can trade only for five days. And should all those five days result in losses, you will go bankrupt. On the contrary, if you take only 2% exposure every day, you can continue to take a position for 50 days. Which do you think is more likely to happen. Losing five trades one after another, or losing 50? You may likely lose five trades one after another. This can go a long way in ensuring long term success by minimizing risk per trade and thus help you with forex risk management.
How much to hedge at one time –
It is an important and difficult decision how much to hedge and when to hedge. Since correctly predicting forex rate is a near impossible task, it is best to hedge over time to minimize being on the wrong side of currency rates. Calculating position sizes is something that a business will need to look at keeping in mind the forex exposures
Stop loss–
Any business taking exposure in forex should set stop losses for forex positions. Stop losses help you control the quantum of losses to a specific level. This is a powerful forex risk management tool in the hand of business. Clarity about stop loss can help contain the losses in case of large scale fluctuations.
Tracking Overall Exposure–
One must keep an eye out on exposure to a particular currency across various transactions. Eg. If you are short on INR/USD and long on USD/JPY, and USD takes a nosedive you will bear losses on both the trades. Keeping overall exposure limited can go a long way in insulating you from the risk of fluctuations and is an important forex risk management technique.
Currency Pair Correlation–
Currencies don’t have a beta. They correlate with other currencies. Like in stocks, beta primarily indicates how much does the stock fall with respect to the index. This helps in ascertaining how risky your stock exposure is. Higher the beta higher the risk. Similarly, in the case of currencies, Correlation in Forex market indicates how changes in one currency reflect in changes in another currency. So you would not want to hedge using currency pairs that are strongly positively correlated because then you would be having more or less, of the same risk and block your margin. You would want to hedge using negatively correlated currency pairs for nullifying the effect of fluctuation. This will help reduce the risk that your exposure brings to your business.
Matching–
Let’s say your organization regularly deals in forex transactions in international trade markets and have payments and incomes to be received in the same currency say USD. In this kind of a scenario, income and expenses can be matched. This results in only unmatched exposures to be hedged in the forex market.
Forward –
Forward is nothing but agreeing to buy or sell an asset like currency in the future at a specified price. The price at which the contract is signed is called forward rate, but the transaction happens at a future date. This helps business in minimizing the forex risk by locking future payments or income today at a fixed rate, thus avoiding risk arising out of currency fluctuations.
Option –
As per a definition, Options are financial instruments that are based on underlying securities such as stocks or currency. That is why they are also called derivatives. An options contract offers the business, an opportunity to buy or sell—depending on the type of contract they hold—the underlying asset. Unlike futures, the business is not required to buy or sell the asset if they choose not to. Using options, a business can hedge risk.
About Cube Edugains –
Forward hedging
Options hedging
LIBOR hedging
ECB hedging
Exchange rate savings in day to day remittances,
Long term foreign exchange hedging,
Currency SWAPS
Large Value Transactions
Check out our services to discover areas that we can help you with
