What is an interest rate cycle?
An interest rate cycle is closely related to the trade or economy cycle. Ideally, movement in interest rates should follow the economic cycle.
Two scenarios play out as far as the interest rate cycle is concerned:
- If the economy is slowing down and inflation also under control and unemployment on the rise, central banks would typically consider cutting down interest rates to provide economic stimulus and hope that the economy starts growing.
- If the economy is witnessing strong growths and inflationary pressures increasing, central banks will increase the interest rate to control inflation. The increased interest rate typically leads to deposit growths and less
In any economy, interest rates are linked to cost of borrowing and lending for a currency.. Interest rates also provide the significant impetus behind the movement of foreign exchange markets. Mostly it is the central bank that controls the economy by controlling the monetary policy that ultimately is driven through interest rates. Most of the Central Banks use interest rates as an instrument of monetary policy to boost economic activity or cut inflationary pressures on the economy. From a forex risk management perspective, it is important to understand how interest rates impact forex exposures.
Impacts of Interest Rates on Foreign Exchange –
As interest rates are cut, It encourages people to spend more. This also results in increasing outflows to countries with higher risk-free return offering countries and thus reduces inflows. This causes a reduction in forex demand and therefore, weakening the currency. It makes the country’s goods cheaper for exports and costlier for imports. This further boosts exports.
Similarly, when central banks are raising interest rates due to inflationary pressures, more forex inflows start moving to country due. This further makes the country’s currency stronger, reducing the exports and making it cheaper to import. Higher rates, therefore, leads to a reduction in inflationary pressures.
Rate cut and hike cycle – .
Rate Cut Cycle –
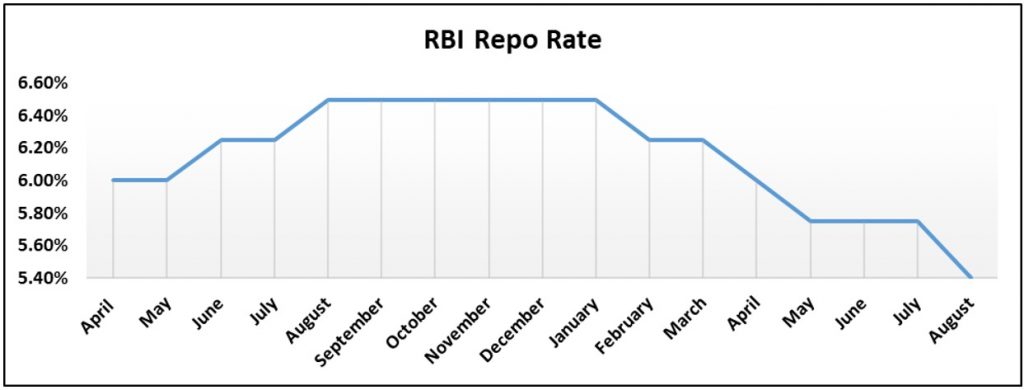
RBI repo rate is a prime example of the rate cut cycle. As you can observe from Jan onwards there has been a downward trend in the Repo rate due to RBI rate cut.
Rate Hike Cycle –
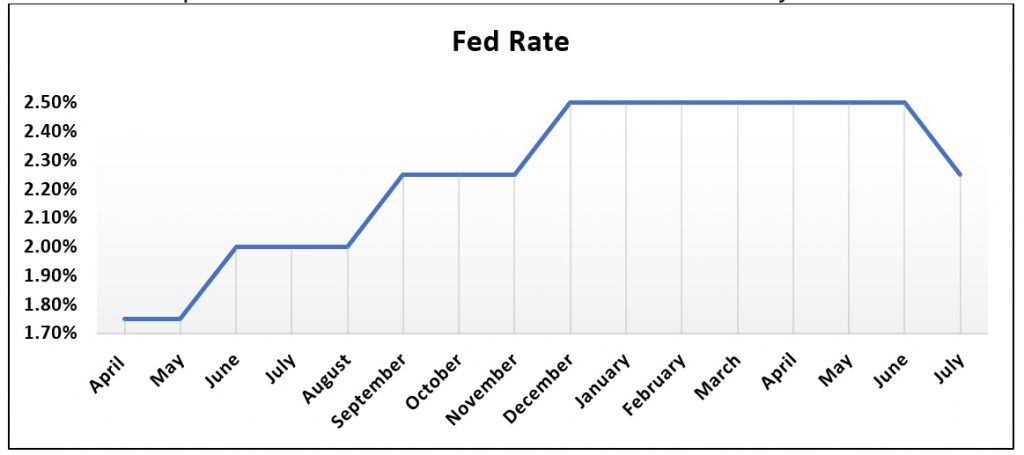
US Fed rate is a prime example of rate hike cycle. As you can since April onwards there has been an upward trend in the Fed rate due to the rate hike by Fed.
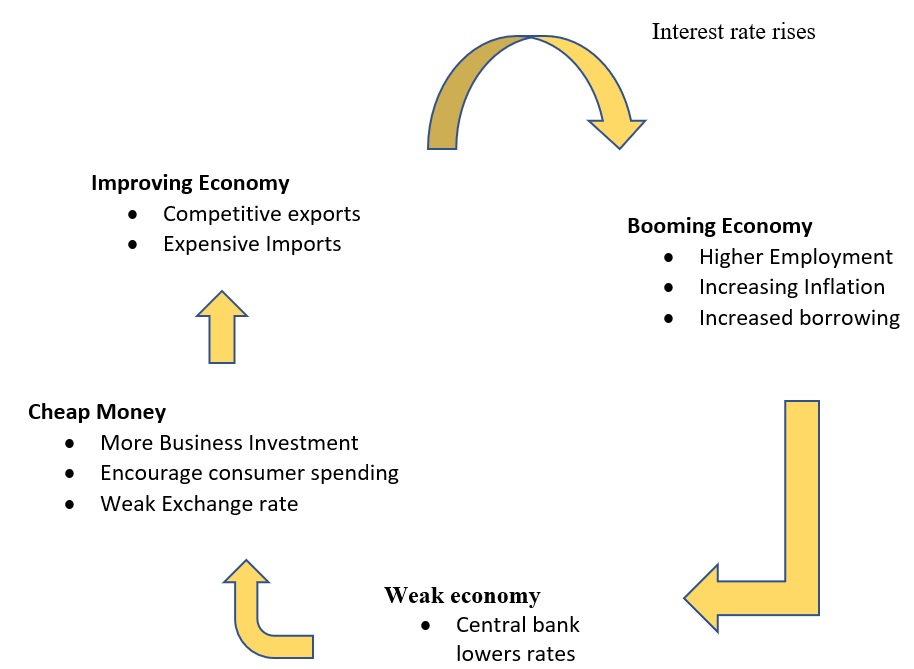
The Central banks use the rate cut or rate hike as a monetary tool. Interest rate can be described as cost of money, like all goods even cost of money decreases when the supply increases.
When the central bank cuts the interest rate, Its their way of telling people to borrow and spend more or continue at the same pace and vice versa happens in the rate hike cycle.
The current trend in rate-cutting cycle:
With US-China Tariff wars and economic slowdown being witnessed in many countries, a lot of central banks have been on an interest rate cutting spree. In India, RBI cut the repo rate by 35bps. There has been four consecutive cuts done by RBI to boost economic activity. The attempt of the rate-cutting cycle is aimed at promoting economic activity and also results in currency to depreciate. Depreciating currency further leads to boosting exports.
